GitLab Deployment¶
Deploying BoostSecurity scanners within GitLab requires careful handling of Docker Hub rate limits and properly configuring self-hosted runners. GitLab jobs often need to pull container images from Docker Hub, which may lead to failures due to anonymous user rate limiting. Additionally, when using self-hosted runners, ensuring correct settings, such as privileged mode, is necessary for successful execution. This document outlines the necessary steps to address these challenges, including authentication methods, dependency proxy configurations, and runner setup.
Docker Hub Pull Rate Limiting¶
When a Boost GitLab job is executed, it often needs to pull a Docker image from Docker Hub. By default, this is done anonymously, making it subject to rate limiting. If the rate limit is exceeded, the job will fail because the required container image cannot be retrieved.
To prevent exceeding the Docker Hub rate limit, there are two main approaches:
1. Authenticate to Docker Hub¶
Organizations with a Docker Hub account can configure GitLab jobs to authenticate to the registry using their account credentials. This can be achieved through the following methods:
-
Using Self-Hosted Runners¶
For self-hosted runners, modify the runner configuration to mount the Docker configuration in each job. Refer to the official GitLab documentation for more details: Mount Docker configuration.
-
Using GitLab SaaS Without Self-Hosted Runners¶
If using GitLab SaaS without self-hosted runners, update each project where the Boost scanner is executed to specify the credentials for pulling from Docker Hub.
Steps:
-
Create a
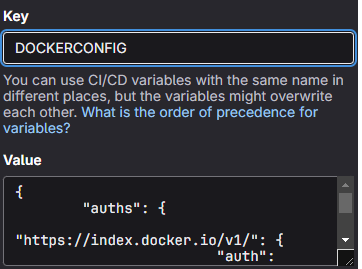
.config.gitlab-ci.ymlfile in your Boost repository with the following content:include: - .gitlab-ci.yml expose_docker_config: stage: .pre script: - echo "DOCKER_CONFIG=$(pwd)/.docker" > dotenv - . dotenv - mkdir -p $DOCKER_CONFIG - cp $DOCKERCONFIG $DOCKER_CONFIG/config.json artifacts: paths: - .docker/config.json reports: dotenv: dotenv -
In Project Settings → CI/CD → Variables, create a file-type CI/CD variable:
-
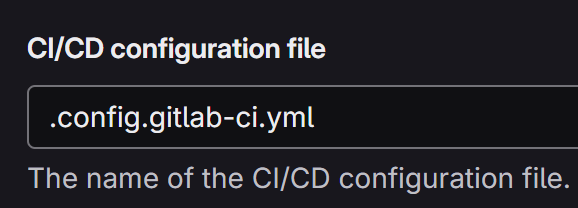
In Project Settings → CI/CD → General pipeline, set the CI/CD configuration file to
.config.gitlab-ci.yml.
2. Use a Docker Container Proxy¶
If you do not have a Docker Hub account, you can set up a dependency proxy for container images in GitLab. Once enabled for the parent group of the Boost repository, configure the Boost scanner to use it by defining the BOOST_DOCKER_PROXY CI/CD variable with the value set to group.
Steps:
Self-Hosted Runners¶
BoostSecurity scanners can be executed using GitLab self-hosted runners. However, additional configuration may be required to ensure proper execution.
Enabling the Privileged Mode¶
To run the Boost GitLab job, the GitLab runner must be able to execute Docker containers. This requires enabling the privileged mode in the runner configuration.
The configuration method depends on the type of GitLab runner agent used. Refer to the GitLab advanced configuration for detailed instructions.
For instance, when using the GitLab Kubernetes agent deployed via the GitLab Helm chart, add the following to the values.yml file:
runners:
config: |
[[runners]]
[runners.kubernetes]
# Run all containers with the privileged flag enabled.
privileged = true
...